What is WCM (World Class Manufacturing) - Pillars and Structure Overview
Oct 28, 2023
World Class Manufacturing (WCM) integrates Operational Excellence methodologies. With 10 managerial and 10 technical pillars, WCM provides a roadmap for leadership, people development, safety, cost reduction, delivery, and quality. Besides, it can be adapted to suit diverse industry needs.
This article will unpack WCM for you. As you go through it, look out for and explore any of the links in green text to understand other related resources.
What is WCM?
WCM represents a comprehensive methodology integrating Lean principles, Total Productive Maintenance pillar concepts, and Total Quality Management. It aims to create an environment of continuous improvement, efficiency, and waste elimination across all operational facets within an organization.
Where did WCM come from?
- Developed through a collaboration between Japanese and Italian professionals and professors in the 1990s to 2000s, it's rooted in lean thinking but tailored for a context outside of Japan.
- It differs from other methodologies (such as Lean and TPM) due to its cultural adaptation and boasts successful cases in companies like Fiat, Chrysler, Unilever, among others, featuring 10 managerial pillars and 10 technical ones.
Who has been successful with it?
- Companies such as Unilever, Fiat, Chrysler, Whirlpool (Brastemp), and Klabin have employed WCM to drive operational excellence and productivity improvements.
- Its application spans various industries, including automotive, manufacturing, consumer goods, and beyond, tailored to suit industry-specific needs.
How does it relate to other CI/OpEx methodologies?
-
Cultural Change: WCM (World Class Manufacturing) is not a project but a way of working. It focuses on eliminating waste and implementing standardized methods within a company's organizational culture.
-
Foundation in Lean and TPM: WCM is similar to methodologies like Lean and TPM (Total Productive Maintenance). The key difference lies in its organizational structure, making the method clearer and more structured, like a recipe.
-
Pillars and Steps: WCM consists of 13 technical pillars and 10 managerial pillars, each with 7 steps that cover reactive, preventive, and proactive phases. Literature may vary, but the structure adapts with industrial evolution.
Structural Framework of WCM:
-
Top Management Involvement: Effective WCM implementation requires the commitment and involvement of top management. The philosophy is implemented from the top down, with managerial leadership playing a crucial role.
Managerial Pillars (10):
- Management Commitment: Involves visible support and active participation from top management, setting the tone for the entire organization to embrace WCM principles.
- Clarity of Objectives: Setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals aligned with the company's vision and strategy.
- Route Map (Development Plan) Crafting a step-by-step plan outlining the implementation stages, key milestones, and responsible stakeholders.
- Allocation of Highly Qualified People: Ensuring the right talent acquisition strategy to bring in individuals with both technical expertise and a mindset aligned with WCM principles.
- Competence of the Organization: Fostering a culture of continuous learning through targeted training programs to equip employees with necessary WCM skills.
- Time and Budget: Allocating resources strategically to support WCM initiatives, recognizing it as an investment for future gains.
- Level of Expansion: Scaling WCM implementation gradually across departments and facilities, ensuring consistent standards.
- Motivation of Associates: Implementing systems to acknowledge and reward individuals or teams demonstrating exemplary WCM practices.
- Level of Detail: achieving depth and advance into more complex opportunities and proactive approaches.
- Commitment of the Organization: ongoing commitment to the journey across all levels of the organization.
Learn how to do items #1 and #8 here to get your organization's ready for WCM: https://www.beltcourse.com/leadership-culture-and-change-simulation
Learn how to do items #2, #3, and #4 here to get going with WCM: https://www.beltcourse.com/strategic-planning-simulation-pl
Learn how to do items #5, #6, and #7 here to deploy WCM across your organization: https://www.beltcourse.com/launch-teams-program
Technical Pillars (10):
- Safety: Incorporating safety protocols and practices to ensure a secure working environment for employees.
- Cost Deployment: Analyzing operational costs meticulously and implementing strategies to reduce unnecessary expenditures.
- Autonomous Maintenance: Establishing autonomous maintenance practices empowering operators to maintain equipment, preventing breakdowns and ensuring optimal functionality.
- Quality Control: Utilizing various quality management tools to maintain and enhance product quality, minimizing defects and errors.
- Logistics and Customer Service: Streamlining supply chain operations, inventory management, and distribution processes for efficiency.
- Environmental: Integrating environmentally sustainable practices, minimizing waste generation and resource consumption.
- People Development: Focusing on employee skill development and talent retention strategies.
- Professional Maintenance: Implementing proactive measures to prevent breakdowns, defects, or inefficiencies.
- Early Equipment Management: Setting and maintaining high product standards to meet customer expectations consistently.
- Focused Improvement: Optimizing resource usage to maximize efficiency and minimize waste in production processes.

Learn how to launch each pillar team here: https://www.beltcourse.com/launch-teams-program
And build each pillar team's competence for their first projects here: https://www.beltcourse.com/first-projects-program-course-page
Impact and Outcomes:
-
Focus on Waste Elimination: The primary goal of WCM is to enhance efficiency by eliminating waste throughout the logistical and production processes. Continuous improvement and smarter work practices naturally lead to better efficiency and results over time.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Resulting in streamlined processes, reduced lead times, and increased productivity.
- Quality Improvements: Consistently delivering products or services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
- Cost Savings: Reduction in operational costs and resource utilization, leading to increased profitability.
- Employee Development: Empowering employees through skill enhancement and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- Sustainable Practices: Contributing to environmental sustainability by reducing the ecological footprint of operations.
Structure and Audit System:
-
Challenging but Feasible: Implementing WCM is not difficult but requires significant effort and discipline. The structured approach (recipe-like methodology) makes it manageable, but it demands cultural change and consistent application.
-
Regular Audits and Evaluations: WCM involves regular audits and evaluations every six months to assess the implementation's effectiveness. These audits are conducted by trained leaders and managers from within the organization or from other companies in the group.
- WCM undergoes audits every six months, aiming for 50 points across technical and managerial pillars, focusing on continuous improvement, although achieving perfection is an objective but rarely accomplished.
- Structured around three technical pillars (reactive, preventive, and predictive), each comprising seven steps, WCM is highly visual and taught through detailed classes or online training programs with mentoring for practical application.
- Although there are benefits of chasing audit scores, there are also major risks and shortcomings.
Learn how to establish internal audits first here, so that you can sustain as you scale: https://www.beltcourse.com/achieving-stability
Customization and Adaptation:
- Adaptation to Industry Needs: Adapting WCM principles to suit the specific demands and challenges of various industries.
- Flexibility in Implementation: Allowing organizations to customize and expand upon the pillars according to their unique organizational structures and requirements.
- Get your own pillar house template and customize it to your organizational structure here.
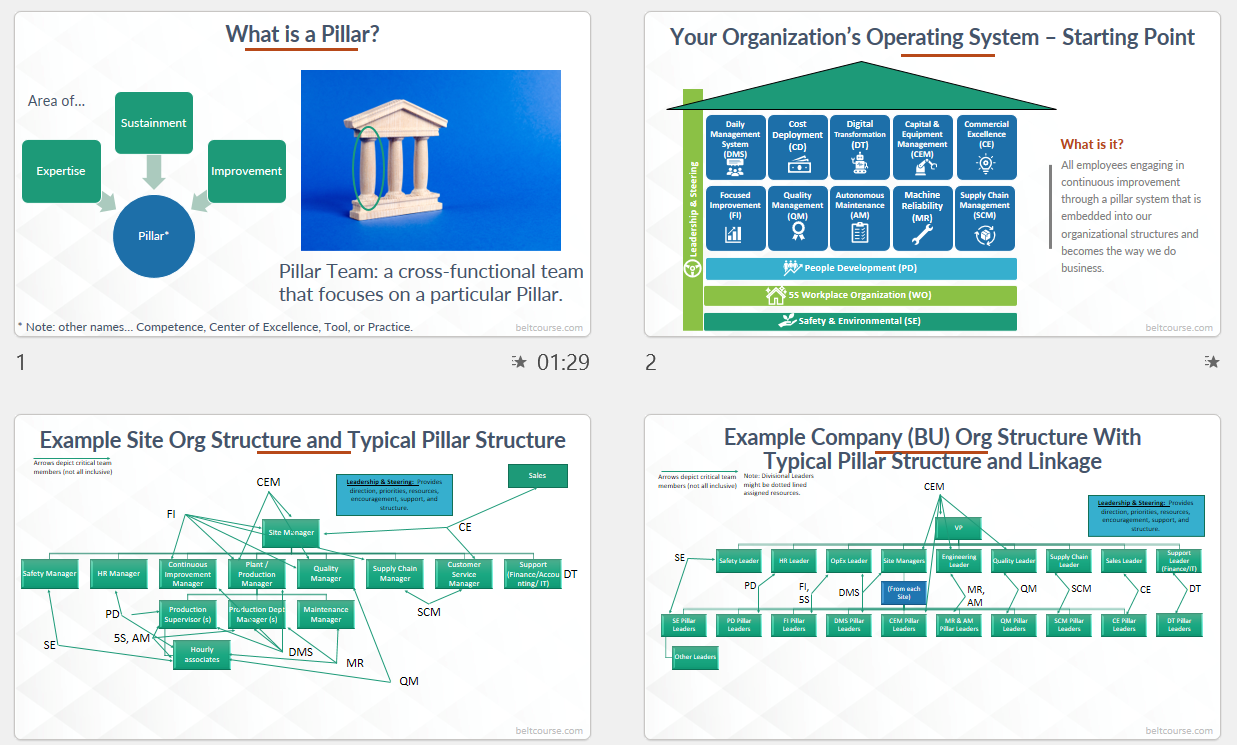
Recent developments in 2025:
- The Japan Institute of Plant Maintenance (JIPM) finally made some adjustments in 2025 to be less prescriptive and to add the pillars that were missing! Those are Supply Chain Management, Digital Transformation, and Environmental.
- WCM already had a "Logistics and Customer Service" pillar, which is similar to SCM.
- WCM already had Environmental.
- WCM didn't have Digital Transformation
- At Belt Course we had already predicted these new pillars, because we've been rolling them out in industries very successfully, and didn't want to be chasing JIPM awards, we wanted to make business impact!
- We have been using coaching programs for these pillars for years!
- If you'd like to learn more about Digital Transformation, for example, visit this page: https://www.beltcourse.com/digital-transformation-intro
- Looking to customize a similar Operating System for your company? Whether you're a Divisional, Regional, Site, Operational Excellence, CI, Department, Pillar, or Project Leader...
-
This program in any language will help top or middle leaders realize why and how to engage all of their workforce to drive cultural change!
- Check out the benefits and trial it at no cost, here: https://www.beltcourse.com/operating-system-and-transformation-program
-
Organizational Structure of WCM:
Implementation and Standard Model:
- Companies follow a basic model when initiating their WCM journey.
- This process involves structuring the team to match or closely resemble the presented standard.
-
Model Areas: Each WCM pillar has its model area tailored to specific needs, such as logistics or machine breakdowns. This focused approach ensures targeted improvements rather than applying the same model area across all pillars.
Team Composition:
- Each team consists of leaders, co-leaders, and members for each technical pillar.
-
Leadership as an Assignment: Being a pillar leader in WCM is an assignment rather than a formal job title. It typically doesn't change your job description or appear in your job title, although some companies hire dedicated WCM specialists.
- Distribution varies based on company size and structure, potentially with a manager overseeing multiple pillars.
Responsibilities and Qualifications:
- Leaders must have expertise in the area they oversee within the company.
- Emphasis on aligning leaders' roles with their specific activities within the realm of WCM.
WCM Support and Connection:
- WCM support serves to assist technical pillars by connecting them with the methodology.
- Focuses on bringing external knowledge to complement and support the pillars in their activities.
-
Employee Knowledge Varies: Not everyone in a company implementing WCM will master the method. Knowledge and understanding of WCM grow as the company progresses through different levels of implementation, such as bronze, silver, and gold.
Focus on Cultural Change:
- The objective is not to add extra work but to drive cultural change within the company.
- This shift is crucial for individuals to perceive WCM as an integral part of their roles.
This breakdown covers the initial structuring to the emphasis on fostering a change in mindset and organizational culture when adopting WCM.
Course Forward:
- Want to Start, re-energize, or adjust a transformation?
- Want to learn how to deploy WCM in your organization?
- Maybe you have opportunities with the managerial pillars...
- Whether you're a Company/Divisional Leader, a Site General Manager, an Operational Excellence Leader, or a Financial Stakeholder...
-
Our OpEx Champion Sponsor coaching program in your language will help you lead your organization through the process, without any false starts!
-
Check out the program and a free 60-day trial here: https://www.beltcourse.com/champion-and-sponsor-curriculum-sp
Additional source:
Did you find this content useful? If you did, you will probably find value in the FREE Tools, Templates, and Mini-Courses we provide to empower you to be successful in your career journey!
Stay connected with news and updates!
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from our team.
Don't worry, your information will not be shared.
We hate SPAM. We will never sell your information, for any reason.


